

Type 4 hiatal hernia is composed of an intrathoracic stomach, which may demonstrate organoaxial rotation. Mixed hiatal hernia (type 3) is a combination of both types 1 and 2 together, with the gastro-oesophageal junction above the hiatus (see Fig. This type of hernia is important because it is more prone to incarceration and obstruction than a sliding hernia.
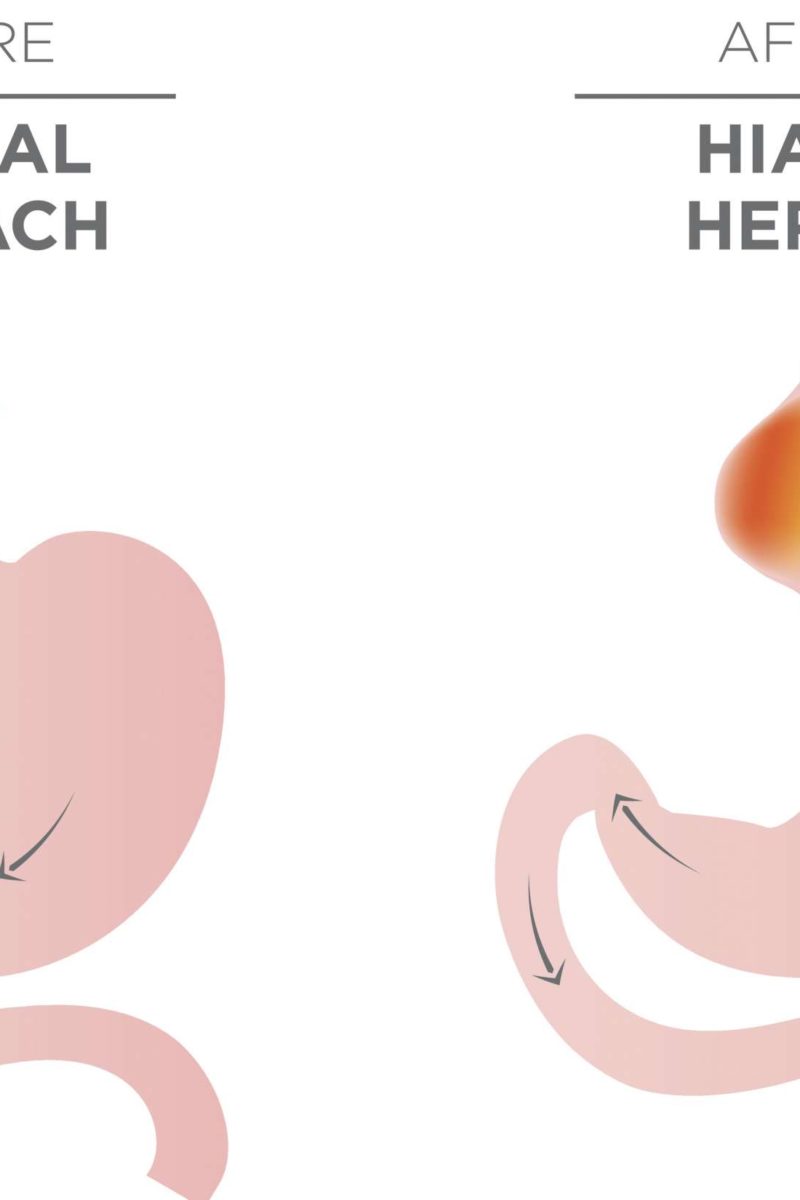

The proximal stomach herniates through the oesophageal hiatus usually to the left of the distal oesophagus in the posterior mediastinum. In comparison to sliding hiatal hernias, in paraoesophageal hernias (type 2) the gastro-oesophageal junction is in its normal position below the diaphragm. Sliding hiatal hernias are often accompanied by gastro-oesophageal reflux and reflux oesophagitis. Small or moderate-sized hiatal hernias are often reducible, changing in size and configuration during barium evaluation and are best demonstrated with the patient recumbent in the right anterior oblique position. In this type of hernia the gastro-oesophageal junction slides proximally through the diaphragmatic hiatus to assume an intrathoracic location. Sliding hiatal hernias are the most common type of hiatal hernia (type 1) (see Fig. Hiatal hernias may be divided into four types ( Fig. At the opposite extreme the entire stomach may be intrathoracic.

Most hiatal hernias are small, involving a protrusion of a part of the gastric fundus at least 1.5 to 2 cm above the diaphragm. The prevalence of hiatal hernia increases with age and is present in over 50% of the aged population. Hiatal hernias are the most common positional abnormality in which the stomach herniates into the chest through the diaphragmatic hiatus when there is widening of the opening between the diaphragmatic crura. These associated problems may require special diagnosis and treatment, and these problems, not the hiatal hernia, are the focus of your physician's attention.Īndreas Adam CBE, MB, BS(Hons), PhD, PhD (hon caus), DSc (hon caus), FRCP, FRCR, FRCS, FFRRCSI(Hon), FRANZCR(Hon), FACR(Hon), FMedSci, in Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology, 2021 Hiatus Hernia Reflux produces heartburn and can cause scarring in the esophagus. Reflux of acid into the esophagus is common with a sliding hiatal hernia. Sliding hiatal hernia occurs with several other medical problems. The hernia itself only rarely causes a health problem, and then only if it is very large. Sliding hiatal hernia does seem to occur with increasing frequency in elderly patients. This type of hiatal hernia is not particularly a problem of elderly patients. The paraesophageal variety may be associated with complications, such as bleeding. Far less common is a variety called a para esophageal hiatal hernia. The most common form is a sliding hiatal hernia. It is a very common finding and occurs in approximately half the adult population of the United States. Sodeman M.D., in Instructions for Geriatric Patients (Third Edition), 2005 General InformationĪ hiatal hernia occurs when the stomach protrudes through the opening in the diaphragm. From Sellke FW et al: Sabiston & Spencer surgery of the chest, ed 9, Philadelphia, 2016, Elsevier. Therefore, this is a type IV hiatal hernia. Three days later, barium is seen in colonic diverticulum on preoperative chest radiograph. From Sellke FW et al: Sabiston & Spencer surgery of the chest, ed 9, Philadelphia, 2016, Elsevier.Ī, Barium esophagram demonstrates a type III hiatal hernia with organoaxial rotation. From Sellke FW et al: Sabiston & Spencer surgery of the chest, ed 9, Philadelphia, 2016, Elsevier.īarium esophagram demonstrates a type III hiatal hernia with organo-axial rotation. From Sellke FW et al: Sabiston & Spencer surgery of the chest, ed 9, Philadelphia, 2016, Elsevier.įIG. Diaphragmatic impression and intrathoracic stomach can be seen. B, Retroflexed view from the intraabdominal stomach at esophagoscopy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
